Main page
About us
Sliding Bearings Consulting
Advertising Opportunities

to Metals
to Metal joining technologies (welding, brazing, soldering)
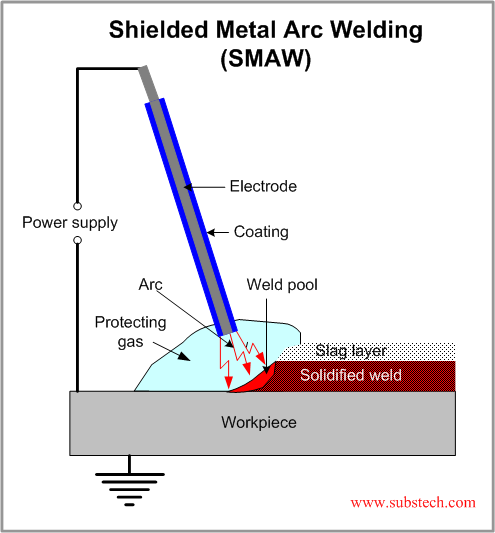
Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW)
Dr. Dmitri Kopeliovich
Shielded metal arc welding (Stick welding, Manual metal arc welding) uses a metallic consumable electrode of a proper composition for generating arc between itself and the parent work piece. The molten electrode metal fills the weld gap and joins the work pieces.
This is the most popular welding process capable to produce a great variety of welds.
The electrodes are coated with a shielding flux of a suitable composition. The flux melts together with the electrode metallic core, forming a gas and a slag, shielding the arc and the weld pool. The flux cleans the metal surface, supplies some alloying elements to the weld, protects the molten metal from oxidation and stabilizes the arc.
The slag is removed after Solidification.
Advantages of Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW):
- Simple, portable and inexpensive equipment;
- Wide variety of metals, welding positions and electrodes are applicable;
- Suitable for outdoor applications.
Disadvantages of Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW):
- The process is discontinuous due to limited length of the electrodes;
- Weld may contain slag inclusions;
- Fumes make difficult the process control.
Related internal links


