to Metals
to Metal forming technologies
Steel strip processing
Dr. Dmitri Kopeliovich
Steel strips are commonly manufactured of continuously cast slabs.
Coiled steel strips have the thickness (gauge) up to 0.2” (5 mm).
The strips are supplied in different conditions:
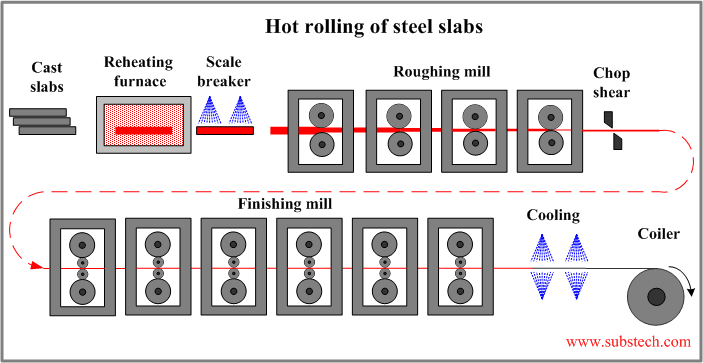
Hot rolling
Continuously cast steel slabs are processed in a hot Rolling line:
- Heating in a gas/oil fired reheating furnace to the temperature 2200-2280ºF (1200-1250ºC).
- Removing oxide scale in a scale breaker. Iron oxides form on the slab surface as a result of high temperature oxidation in the reheating furnace. Scale breaker utilizes high pressure water jets directed to the slab surface.
- Finishing rolling in a tandem four-high rolling mill (5-7 stands). The strip dimensions (thickness, width) are strictly controlled in this operation.
- Cooling by water jets. The temperature is reduced to max. 1110ºF (600ºC).
- Coiling the finished strip. Hot rolled strips have a thin scale of iron oxides on their surface. Part of the strips is used in as-rolled condition. Other part is processed in a pickling line where the oxide scale is removed.
Pickling of steel strip
Hot rolled strip is treated in a pickling line:
- Uncoiling.
- Pickling in a solution of hydrochloric or sulfuric acid. The acid dissolutes the oxide scale from the strip surface according to the reaction: Fe2O3 + 6HCl = 2FeCl3 + 3H2O.
- Rinsing and passivation of the strip. At this stage the acid residuals are washed by water from the strip. Passivation film is formed on the strip surface providing corrosion protection.
- Drying.
- Edge trimming.
- Oiling.
- Recoiling.
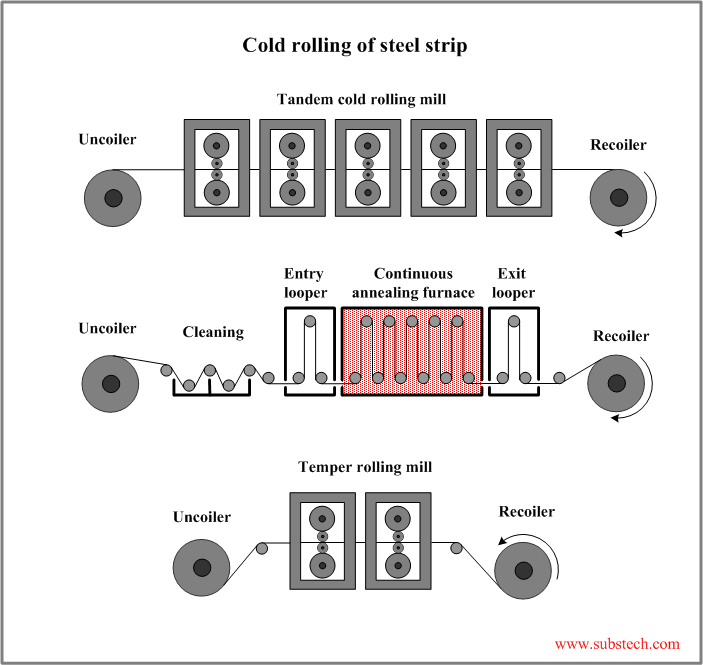
Cold rolling of steel strip
Cold rolled steel strips are used mainly in the Deep drawing process.
The purposes of cold rolling processing are:
- Further reduction of the strip thickness;
- Improvement of the surface finish;
- Improvement of the surface flatness;
- Achievement of a required level of work hardening.
Cold rolling processing includes the following stages:
- Cold rolling in a tandem rolling mill. The rolling mill consists of 5-7 stands having four-high configuration (two large back-up rolls and two small work rolls).
- Annealing at a temperature 1100-1300ºF (600-700ºC) in a controlled reducing atmosphere (commonly a mixture of Hydrogen and Nitrogen) preventing oxidation of the steel surface. Annealing results in recrystallization of the steel Grain structure and in stress relief. There are two alternatives of annealing process: continuous annealing line and batch annealing furnace. In the continuous annealing line (see the picture below) steel strip passes annealing furnace at a controlled speed. In the batch process steel strip coils are stacked on top of each other in the bell type furnace. Batch annealing allows to achieve lower hardness and higher ductility of the steel than in alternative continuous annealing.
- Temper rolling (skin pass rolling) - final cold rolling operation with low thickness reduction conducted in order to impart to the steel required levels of hardness, evenness and surface finish. Four-high rolling mill is used for tempering.
Most of annealed low carbon steel strips are tempered since they are too soft (HV<110) in annealed condition. Bending and deep drawing operations of soft annealed steel may cause formation of kinks (cross breaks) and stretcher strains, which are the result of localized stretching of the strip at low cold deformation beyond the yield point. Light tempering of annealed strip (non-kinking temper, pinch pass) produces strip surface conditions, which do not cause formation of cross breaks and stretcher strains. Hardness of pinch passed steel is about 115 HV. Other temper conditions of steel strip are: eighth hard (105<HV<125), quarter hard (115<HV<130), half hard (130<HV<160), three quarter hard (150<HV<185).
Surface finish conditions of cold rolled steel strip:
- Mirror. Superior luster mirror finish is produced by rolling between fine polished rolls. Mirror finish strips are used mainly for electroplating.
- Bright. Bright finish is produced by rolling between polished rolls. It is the common surface finish condition of cold rolled strip.
- Matt. Matt (dull) surface finish is produced by rolling between roughened rolls. Matt surface is suitable for enameling and painting. Matt finish strips are also used in deep drawing due to the ability of the rough surface to hold lubricant providing low friction between the strip and the drawing tools (punch, blank holder, die).
- Blued. Blued surface finish is produced by controlled heating and cooling of bright finish strip resulting in formation of thin blue oxide film on the steel surface.
Strip edges conditions:
- Natural mill edges, which are result of cold rolling without any edge cutting operation. Natural mill edges may have micro-cracks due to non-uniform work hardening.
- Slit edges (shared edges), which are produced by rotary slitter. Slit edges are square with slight sharp burr.
- Dressed edges - slit edges, from which burr has been removed.
- Rolled edges, which are formed by edge rolling.
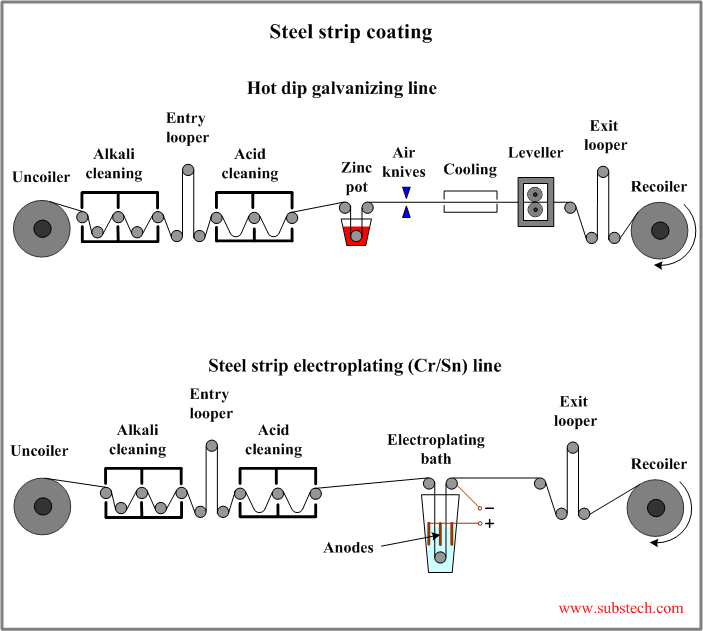
Steel strip coating
The most popular techniques of continuous steel strip coating are hot dip galvanizing and Electroplating.
Hot dip galvanizing process
- Uncoiling.
- Cleaning. This operation commonly combines Alkaline cleaning (degreasing) and mechanical cleaning by rotating cylindrical brushes. Oil and other contaminants are removed from the steel surface.
- Pickling. Degreased and rinsed strip enters a pickling bath where oxides and rust are dissolved by hydrochloric acid and removed according to the reactions:
Iron oxide reaction: Fe2O3 + 6HCl = 2FeCl3 + 3H2O
Rust reaction: Fe2O3*nH2O + 6HCl = 2FeCl3 + (n+3)H2O
- Zinc coating (hot galvanizing). Clean strip passes through a bath with molten zinc (Zn).
- Wiping excessive zinc by air knives.
- Cooling. The coated strip is cooled by air and water.
- Levelling. Leveller produces smooth and flat strip surface.
- Recoiling.
Continuous electroplating process
- Uncoiling.
- Cleaning. This operation commonly combines alkaline cleaning (degreasing) and mechanical cleaning by rotating cylindrical brushes. Oil and other contaminants are removed from the steel surface.
- Pickling. Degreased and rinsed strip enters a pickling bath where oxides and rust are dissolved by hydrochloric acid and removed according to the reactions:
Iron oxide reaction: Fe2O3 + 6HCl = 2FeCl3 + 3H2O
Rust reaction: Fe2O3*nH2O + 6HCl = 2FeCl3 + (n+3)H2O
- Electroplating. Clean strip passes through a series of vertical electroplating baths. The strip is connected to the DC power supply as a cathode (negative). The positively connected anodes are arranged in parallel to the strip opposite to its surface. The bath is filled with an electrolytic solution. Electrolyte and anodes compositions are determined by the the deposited material and the electroplating method (Tin alloy electroplating, Decorative chromium electroplating|chromium electroplating, zinc electroplating).
- Recoiling.